Next gen firewalls include such functionality as:
deep packet inspection which is checking the actual contents of the data packet, TCP handshake checks, and surface level packet inspection. Many next-generation firewalls could be considered intrusion prevention
systems - IPSs - which can halt attacks against networks.
Firewalls are normally placed between a protected network and an unprotected network and acts like a gate to protect assets to
ensure that nothing private goes out and nothing malicious comes in.
A firewall's basic task is to regulate some of the flow of traffic between
computer networks of different trust levels. Typical examples are the
Internet which is a zone with no trust and an internal network which is a zone of higher trust. A zone
with an intermediate trust level, situated between the Internet and a trusted internal network, is often referred to as a
"perimeter network" or Demilitarized zone (DMZ).
Firewalls function within networks are area similar to physical firewalls with fire doors in building construction. In the
former case, it is used to prevent network intrusion to the private network. In the latter case, it is intended to contain
and delay structural fire from spreading to adjacent structures.
This is the Cisco Firepower 2140 which is one of Cisco's high end firewalls and lists for about $45,000.00

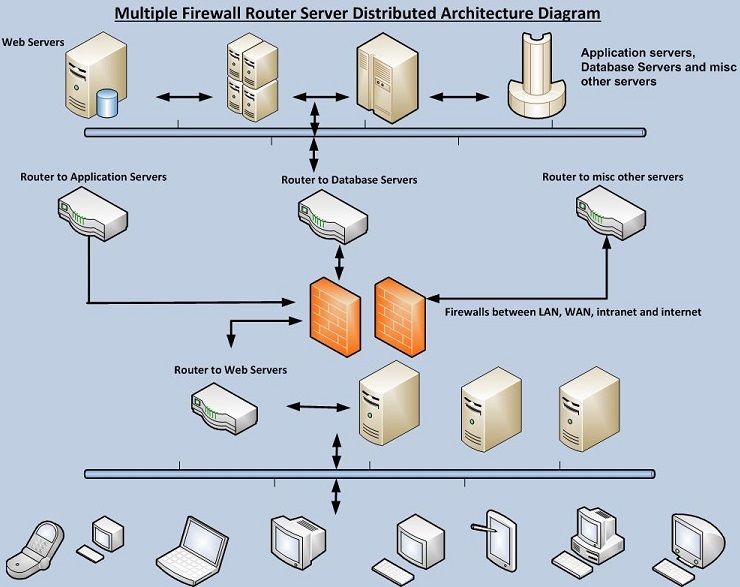
This diagram displays how firewalls can be placed between
network segments in order to protect different network segments.